This article takes a deep dive into the Emotet virus Mac, covering its propagation, characteristics, adverse effects, and providing a viable removal method.
Update:
Emotet is a harmful virus, also categorized as a trojan, that affects Macs and PCs in several different ways. Its main goal is to harvest and steal confidential information, such as banking credentials, passwords for email clients and other online accounts, as well as details related to cryptocurrency wallets, to name a few. In fact, this heinously operating malicious code was originally created as banking malware, and it continues to go down that slope while exhibiting several extra capabilities acquired in the course of its evolution. The info-stealer component has been complemented with a virus spreading functionality, which means that the menace can deposit other cyber infections onto contaminated Macs without raising any red flags visible to the naked eye. Besides, Emotet is extremely sneaky when it comes to automatic detection, because it uses a different file manifestation, that is, executable name, on different polluted hosts.
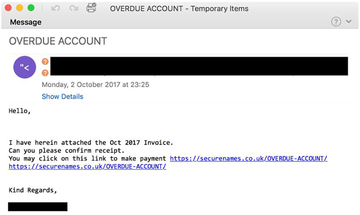
The way the Emotet virus infects Mac computers resembles a continuous loop. The main entry point is malicious spam. The cybercriminals use a nefarious capacity of a botnet to send out tens of thousands of trojanized emails in one hit. These messages appear to be competently tailored and can be disguised as an invoice, subscription terms change, tax return transcript, new order notification, overdue account alert or something similar that evokes curiosity. The recipient who gets on the hook will proceed to the attached or linked-to file, which is a Mac-compatible Word document. As soon as this toxic object is downloaded and opened, it is presented as a blank document that doesn’t render any contents because macros are disabled. In this case, the system is configured to display a dialog asking the user whether they agree to enable macros. This is an unreasonable thing to do, especially if a fishy-looking email attachment is asking for this.
Word macros are known to be particularly vulnerable to unauthorized tampering. When abused, they can facilitate surreptitious downloading of malicious code from a remote server. This is what happens in the Emotet virus attack scenario. The adversaries covertly drop a copy of the disruptive executable onto a Mac, which then follows a predefined modus operandi. Its polymorphic nature allows it to mutate from incursion to incursion and thereby stay undetected by the traditional signature-based security utilities. The virus will also add itself to the login items to maintain persistence. When running, it performs a kind of reconnaissance on the Mac to find potentially sensitive information. Again, it is mainly after the victim’s logins and passwords for their online banking accounts, but additionally targets all the other credentials it can find.
Emotet may re-infect your Mac multiple times unless you delete all of its fragments, including hidden ones. Therefore, it is recommended to download Combo Cleaner and scan your system for these stubborn files. This way, you may reduce the cleanup time from hours to minutes.
Download Now Learn how Combo Cleaner works. If the utility spots malicious code, you will need to buy a license to get rid of it.This threat exhibits worm-like characteristics allowing it to expand the attack surface very quickly. Upon contamination, Emotet can hand a copy of itself over to the other Macs on the same network. This is an extremely serious concern for organizations and local governments, because they run the risk of falling victim to a network-wide onslaught affecting tens of thousands of machines. The malady has a built-in brute force module, which allows it to crack system access passwords on its way to large-scale propagation. According to the U.S. Department of Homeland Security (DHS), remediation of one Emotet-backed cyber raid affecting a local government costs $1 million on average. This is due to the considerable footprint the virus causes network-wise, making it extremely difficult and time-consuming to eradicate the dangerous code and revert to normal operation. To top it all off, this is a VM-aware culprit and therefore it hides its tracks when executed in a virtual machine environment. There are very few malware strains out there that can boast such a sophisticated antivirus evasion toolkit.
Another noteworthy feature is the ability to communicate with a Command & Control server, which is the entity that actually issues commands and sends other malicious items to the infected computers. The latter, by the way, is a growingly disconcerting trend making itself felt at this point. The perpetrators can inject more parasites into the tainted Macs, including keyloggers, crypto ransomware, adware, and rogue system utilities. All in all, Emotet poses a huge risk to individual Mac users and companies alike. The sooner the victim completes the cleanup the more likely they are to keep their privacy and personal funds intact.
Emotet virus manual removal for Mac
The steps listed below will walk you through the removal of this unwanted application. Be sure to follow the instructions in the order specified.
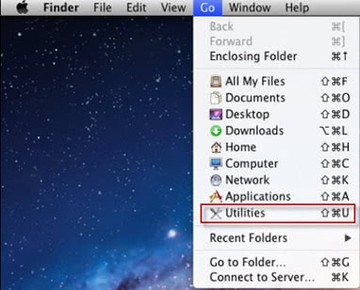
• Open up the Utilities folder as shown below
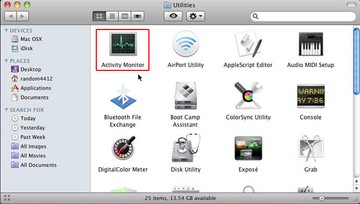
• Locate the Activity Monitor icon on the screen and double-click on it
• Under Activity Monitor, find a suspicious-looking entry and click Quit Process
• A dialog should pop up, asking if you are sure you would like to quit the misbehaving executable. Select the Force Quit option
• Click the Go button again, but this time select Applications on the list. Find the entry likely related to Emotet on the interface, right-click on it and select Move to Trash. If user password is required, go ahead and enter it

• Now go to Apple Menu and pick the System Preferences option
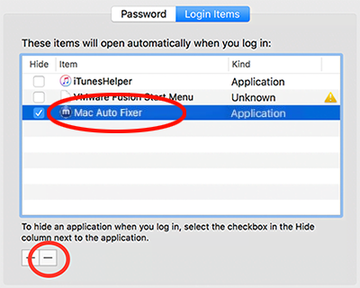
• Select Accounts and click the Login Items button. The system will come up with the list of the items that launch when the box is started up. Locate the malicious item there and click on the “-“ button
Use automatic tool to remove Emotet virus from your Mac
The Mac maintenance and security app called Combo Cleaner is a one-stop tool to detect and remove Emotet virus. This technique has substantial benefits over manual cleanup, because the utility gets hourly virus definition updates and can accurately spot even the newest Mac infections.
Furthermore, the automatic solution will find the core files of the malware deep down the system structure, which might otherwise be a challenge to locate. Here’s a walkthrough to sort out the Emotet issue using Combo Cleaner:
Download Combo Cleaner installer. When done, double-click the combocleaner.dmg file and follow the prompts to install the tool onto your Mac.
By downloading any applications recommended on this website you agree to our Terms and Conditions and Privacy Policy. The free scanner checks whether your Mac is infected. To get rid of malware, you need to purchase the Premium version of Combo Cleaner.
Open the app from your Launchpad and let it run an update of the malware signature database to make sure it can identify the latest threats.
Click the Start Combo Scan button to check your Mac for malicious activity as well as performance issues.

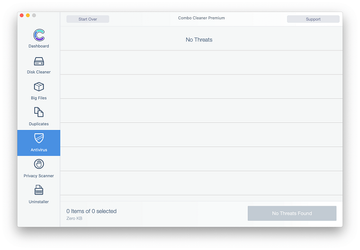
Examine the scan results. If the report says “No Threats”, then you are on the right track with the manual cleaning and can safely proceed to tidy up the web browser that may continue to act up due to the after-effects of the malware attack (see instructions above).
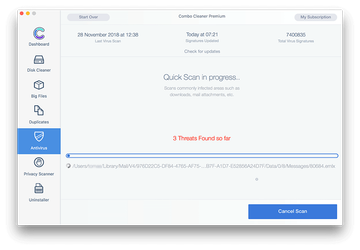
In case Combo Cleaner has detected malicious code, click the Remove Selected Items button and have the utility remove Emotet threat along with any other viruses, PUPs (potentially unwanted programs), or junk files that don’t belong on your Mac.
Once you have made doubly sure that the malicious app is uninstalled, the browser-level troubleshooting might still be on your to-do list. If your preferred browser is affected, resort to the previous section of this tutorial to revert to hassle-free web surfing.
FAQ
Can a Mac get a Trojan virus?
Yes, it can. Technically speaking, a Trojan virus is a form of malicious code that infects computers by posing as a benign application or a required software update. In fact, the vast majority of Mac threats are doing the rounds via this technique. The logic of such an attack is to dupe the user into thinking they are installing something harmless or even useful, with the infection chain taking place behind the scenes.
One of the notorious Mac Trojans is called Flashback. In 2012, it reportedly plagued more than 600,000 Macs by means of a phony Adobe Flash Player update advertised on malicious and hacked websites. Once on board a system, Flashback looks for and pilfers passwords along with other confidential data.
When it comes to Emotet, the distribution mostly relies on virus-riddled Word files arriving with spam. These email attachments can be masqueraded as a license agreement acceptance, invoice, tax form, missed delivery notice, job offer, and many other file types that tend to grasp one’s attention. In a few recent campaigns, these messages would even address the recipients by name, siphoning data from service breaches perpetrated in the past.
The booby-trapped documents don’t display any intelligible content unless the user enables macros using an appropriate prompt that pops up automatically. However, turning macros on instantly executes a script that downloads a copy of Emotet onto the Mac. This is an example of a classic Trojan attack that capitalizes on social engineering to trigger a dodgy download. It demonstrates the viability of this malware distribution vector in the Mac realm. Again, Trojans do infect Mac computers, and this mechanism is becoming increasingly common.
What is Trojan Emotet?
Emotet is a sophisticated Trojan horse predominantly targeting Microsoft Windows computers while featuring macOS compatibility as well. Originally operating as a banking Trojan, it aims to harvest victims’ sensitive information and send it to cybercriminals. Since 2014, when Emotet was discovered, it has been equipped with extra functionality allowing it to drop follow-up malware onto the infected machine. The secondary payloads include other info-stealers, ransomware, and adware, to name a few.
This Trojan is polymorphic, which means it can additionally manifest itself as a worm in terms of self-distribution. Once it gains a foothold in a computer network, it can replicate itself to all the nodes in no time. This is a serious roadblock to cleaning up a compromised enterprise or government ecosystem consisting of numerous computers. The polymorphic gist of this pest also allows it to get around traditional signature-based detection.
Trojan Emotet maintains communication with its C2 server to perform exfiltration of the collected sensitive data and receive commands of its operators. This interaction is also a means of cross-promoting affiliated threats after the initial incursion, the malicious server being a source of the opportunistic malware downloads.
To recap, Emotet is one of the most evasive and harmful Trojans in circulation these days. It poses a serious risk to victims’ financial credentials and disseminates other viruses to ensure a maximum monetization of every infection instance.
