In a recent move, a group of seasoned Mac adware makers added search-location.com webpage to their ever-expanding browser redirect repertoire.
What is the search-location.com virus?
A good way to grasp the undercurrents of the search-location.com browser rerouting scheme is to look into the murky waters of an overlapping malware campaign that has gained notoriety for being incredibly irksome and prolific over the years. Those initiated in the top security concerns across the macOS ecosystem are well aware of Search Marquis, a strain that hijacks web browsers and drives traffic to Bing or other services the victims never opted into using. It turns out that the ties between these two entities are as close as the relation between senior and subordinate. Specifically, search-location.com is just another in-between spot in the browser redirect chain triggered by the Search Marquis virus. When a Mac is hit, a trio of the most popular browsers – Safari, Google Chrome, and Mozilla Firefox – are quietly reconfigured so that wrong URLs are resolved during regular Internet sessions, in general, and web searches, in particular.
An observant user will notice a series of weird strings in the address bar along the way. Besides search-location.com, these may include searchbaron.com, nearbyme.io, api.lisumanagerine.club, and search1.me. In most cases, the final destination is a legitimate search engine results page (SERP) provided by Microsoft’s Bing. The catch behind the incorporation of this reputable service in the crooks’ dirty scheme is to smokescreen all the preceding shadowy events and thereby make victims less suspicious. In the meanwhile, every instance of momentarily visiting the sketchy domains fuels a traffic monetization stratagem that involves dubious ad processing networks. Plus, Bing has an affiliate program of its own, and this could also be a lure to light-fingered individuals such as search-location.com authors.
Search-location.com virus may re-infect your Mac multiple times unless you delete all of its fragments, including hidden ones. Therefore, it is recommended to download Combo Cleaner and scan your system for these stubborn files. This way, you may reduce the cleanup time from hours to minutes.
Download Now Learn how Combo Cleaner works. If the utility spots malicious code, you will need to buy a license to get rid of it.To expand the dodgy marketing reach, the gang additionally mishandles custom search opportunities stemming from other popular providers. The above-mentioned search1.me page is a good example (see the screen capture below). Regardless of the specific “flavor” of this long-running campaign and the landing pages swapping periodically, the objective is the same – to gain illicit profit by taking advantage of the infected Mac machines. Speaking of which, the search-location.com redirect virus tends to arrive in the shape of a harmless-looking trojanized application pushed via rogue ads. It may also spread as part of bundles whose installation clients only disclose the benign components and hush up the dangerous one.
When the malicious object crops up inside a Mac without the user’s consent, it sprinkles its files across the system, including in the Launch Agents, Launch Daemons, and Application Support directories. It is also equipped with a data harvesting module that tracks down one’s Internet history, the Mac’s hardware and software specifications, location info, and more. Since the culprit largely focuses on the web surfing side of things, it creates a device profile that imposes unwanted web search, homepage, and new tab preferences in the victim’s default browser. This trick is the foundation of Search Marquis’ persistence, because many users unfamiliar with the “Profiles” feature keep tidying up specific affected settings in Safari, Chrome, or Firefox, only to realize that the wrong properties are back shortly.
The good news is, the virus is not that hard to vanquish as long as a well-thought-out cleaning procedure kicks in. The following steps compose an effective mechanism to get rid of search-location.com and fix the associated security issues such as possible identity theft, system performance impact, and the infiltration of extra payloads that plague the Mac with more malware.
Search-location.com virus popup manual removal for Mac
The steps listed below will walk you through the removal of this malicious application. Be sure to follow the instructions in the specified order.
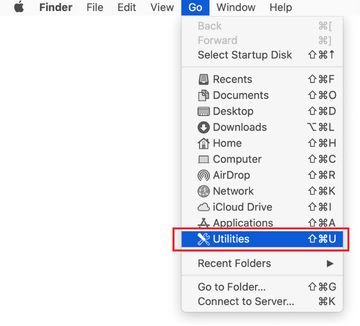
Expand the Go menu in your Mac’s Finder bar and select Utilities as shown below.
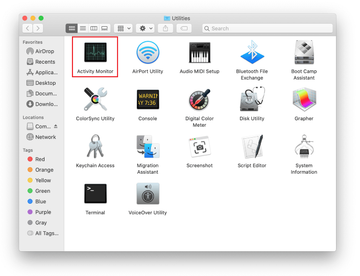
Locate the Activity Monitor icon on the Utilities screen and double-click on it.
In the Activity Monitor app, look for a process that appears suspicious. To narrow down your search, focus on unfamiliar resource-intensive entries on the list. Keep in mind that its name isn’t necessarily related to the way the threat is manifesting itself, so you’ll need to trust your own judgement. If you pinpoint the culprit, select it and click on the Stop icon in the upper left-hand corner of the screen.
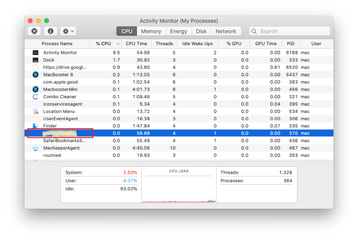
When a follow-up dialog pops up asking if you are sure you want to quit the troublemaking process, select the Force Quit option.
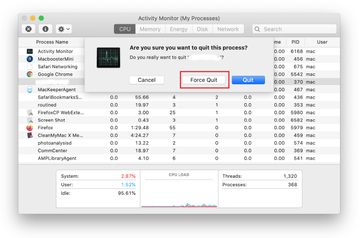
Click on the Go menu icon in the Finder again and select Go to Folder. You can as well use the Command-Shift-G keyboard shortcut.
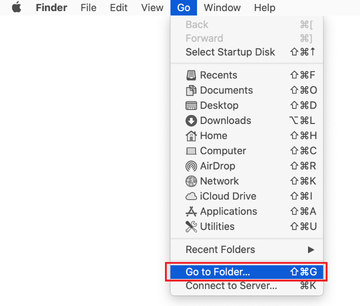
Type /Library/LaunchAgents in the folder search dialog and click on the Go button.
Examine the contents of the LaunchAgents folder for dubious-looking items. Be advised that the names of files spawned by malware may give no clear clues that they are malicious, so you should look for recently added entities that appear to deviate from the norm.
As an illustration, here are several examples of LaunchAgents related to mainstream Mac infections: com.updater.mcy.plist, com.avickUpd.plist, and com.msp.agent.plist. If you spot files that don’t belong on the list, go ahead and drag them to the Trash.
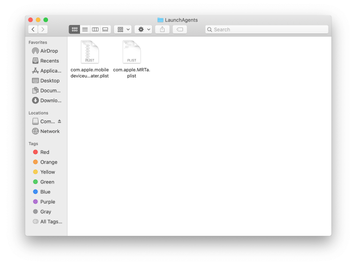
Use the Go to Folder lookup feature again to navigate to the folder named ~/Library/Application Support (note the tilde symbol prepended to the path).
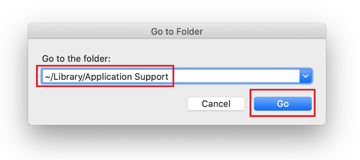
When the Application Support directory is opened, identify recently generated suspicious folders in it and send them to the Trash. A quick tip is to look for items whose names have nothing to do with Apple products or apps you knowingly installed. A few examples of known-malicious folder names are com.AuraSearchDaemon, ProgressSite, and IdeaShared.
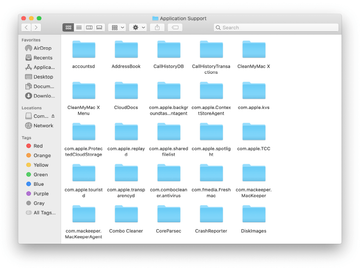
Enter ~/Library/LaunchAgents string (don’t forget to include the tilde character) in the Go to Folder search area.
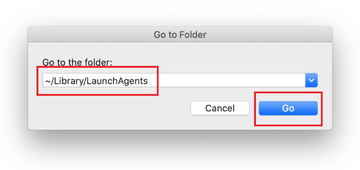
The system will display LaunchAgents residing in the current user’s Home directory. Look for dodgy items related to search-location.com redirect virus (see logic highlighted in subsections above) and drag the suspects to the Trash.
Type /Library/LaunchDaemons in the Go to Folder search field.
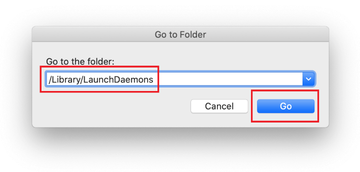
In the LaunchDaemons path, try to pinpoint the files the malware is using for persistence. Several examples of such items cropped by Mac infections are com.pplauncher.plist, com.startup.plist, and com.ExpertModuleSearchDaemon.plist. Delete the sketchy files immediately.
Click on the Go menu icon in your Mac’s Finder and select Applications on the list.
Find the app that clearly doesn’t belong there and move it to the Trash. If this action requires your admin password for confirmation, go ahead and enter it.

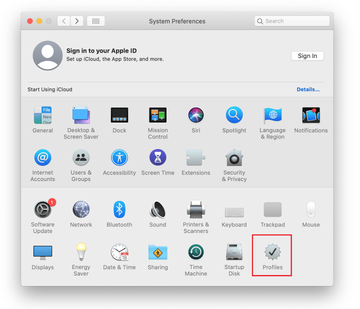
Expand the Apple menu and select System Preferences.
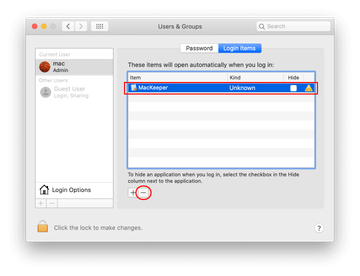
Proceed to Users & Groups and click on the Login Items tab.
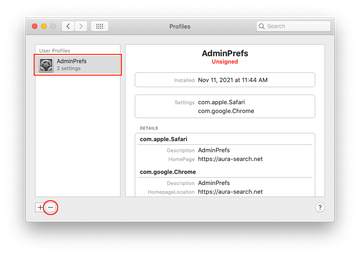
Now select Profiles under System Preferences. Look for a malicious item in the left-hand sidebar. Several examples of configuration profiles created by Mac adware include TechSignalSearch, MainSearchPlatform, AdminPrefs, and Safari Preferences. Select the offending entity and click on the minus sign at the bottom to eliminate it.
Get rid of search-location.com virus in web browser on Mac
To begin with, the web browser settings taken over by the search-location.com virus should be restored to their default values. Although this will clear most of your customizations, web surfing history, and all temporary data stored by websites, the malicious interference should be terminated likewise. The overview of the steps for completing this procedure is as follows:
- Remove search-location.com virus from Safari
Open the browser and go to Safari menu. Select Preferences in the drop-down list.
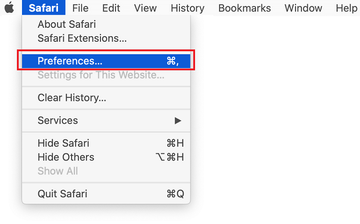
Once the Preferences screen appears, click on the Advanced tab and enable the option saying “Show Develop menu in menu bar”.
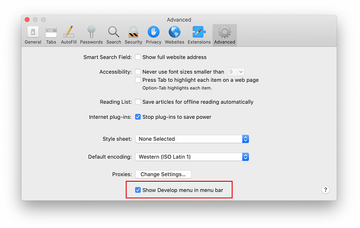
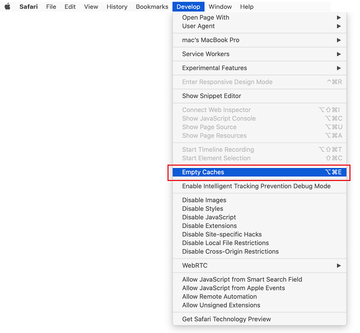
Now that the Develop entry has been added to the Safari menu, expand it and click on Empty Caches.
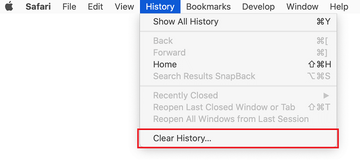
Now select History in the Safari menu and click on Clear History in the drop-down list.
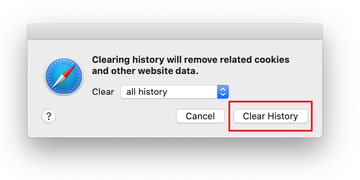
Safari will display a dialog asking you to specify the period of time this action will apply to. Select all history to ensure a maximum effect. Click on the Clear History button to confirm and exit.
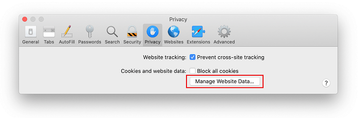
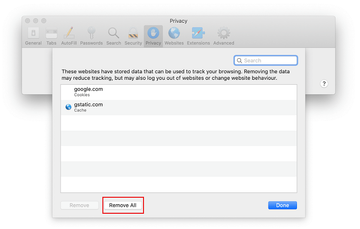
Go back to the Safari Preferences and hit the Privacy tab at the top. Find the option that says Manage Website Data and click on it.
The browser will display a follow-up screen listing the websites that have stored data about your Internet activities. This dialog additionally includes a brief description of what the removal does: you may be logged out of some services and encounter other changes of website behavior after the procedure. If you’re okay with that, go ahead and click on the Remove All button.
Restart Safari
- Remove search-location.com in Google Chrome
Open Chrome, click the Customize and control Google Chrome (⁝) icon in the top right-hand part of the window, and select Settings in the drop-down
When on the Settings pane, select Advanced
Scroll down to the Reset settings section.
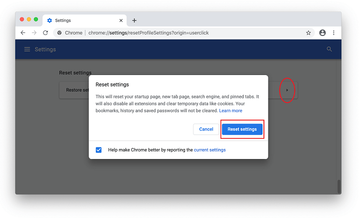
Confirm the Chrome reset on a dialog that will pop up. When the procedure is completed, relaunch the browser and check it for malware activity.
- Remove search-location.com from Mozilla Firefox
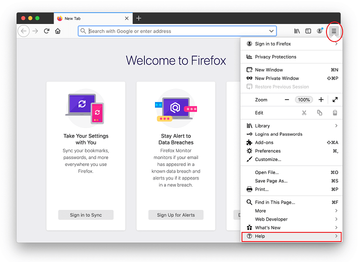
Open Firefox and go to Help – Troubleshooting Information (or type about:support in the URL bar and press Enter).
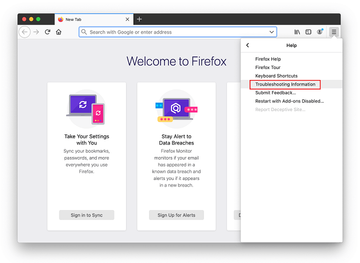
When on the Troubleshooting Information screen, click on the Refresh Firefox button.
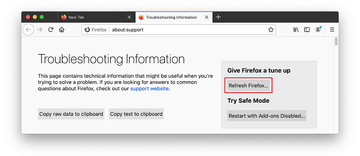
Confirm the intended changes and restart Firefox.
Get rid of search-location.com virus using Combo Cleaner removal tool
The Mac maintenance and security app called Combo Cleaner is a one-stop tool to detect and remove search-location.com virus. This technique has substantial benefits over manual cleanup, because the utility gets hourly virus definition updates and can accurately spot even the newest Mac infections.
Furthermore, the automatic solution will find the core files of the malware deep down the system structure, which might otherwise be a challenge to locate. Here’s a walkthrough to sort out the search-location.com issue using Combo Cleaner:
Download Combo Cleaner installer. When done, double-click the combocleaner.dmg file and follow the prompts to install the tool onto your Mac.
By downloading any applications recommended on this website you agree to our Terms and Conditions and Privacy Policy. The free scanner checks whether your Mac is infected. To get rid of malware, you need to purchase the Premium version of Combo Cleaner.
Open the app from your Launchpad and let it run an update of the malware signature database to make sure it can identify the latest threats.
Click the Start Combo Scan button to check your Mac for malicious activity as well as performance issues.

Examine the scan results. If the report says “No Threats”, then you are on the right track with the manual cleaning and can safely proceed to tidy up the web browser that may continue to act up due to the after-effects of the malware attack (see instructions above).
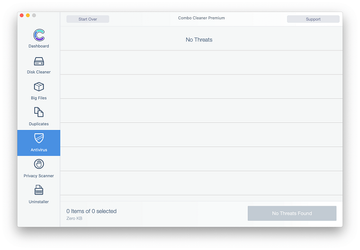
In case Combo Cleaner has detected malicious code, click the Remove Selected Items button and have the utility remove search-location.com threat along with any other viruses, PUPs (potentially unwanted programs), or junk files that don’t belong on your Mac.
Once you have made doubly sure that the malicious app is uninstalled, the browser-level troubleshooting might still be on your to-do list. If your preferred browser is affected, resort to the previous section of this tutorial to revert to hassle-free web surfing.
